Fifth-generation (5G) technology represents a significant advancement in mobile communication systems, fundamentally altering the landscape of connectivity. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is designed to meet the growing demand for higher data speeds, reduced latency, and increased connectivity for a multitude of devices. The key characteristic that sets 5G apart from earlier generations, such as 4G LTE, is its ability to support a vast number of connections simultaneously, making it particularly essential for the burgeoning Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.
One of the most notable features of 5G is its remarkable speed. The technology is capable of delivering data transfer rates of up to 10 Gbps, far surpassing the theoretical limits of 4G. This acceleration enables seamless streaming of high-definition content and enhances the experience of using connected devices within smart homes. Furthermore, 5G employs advanced technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output) and beamforming, which optimize signal quality and expand coverage areas, allowing for strong connectivity even in denser environments.
Lower latency is another critical aspect of 5G technology. With latency levels potentially dropping as low as 1 millisecond, real-time communication becomes feasible, greatly benefiting applications that require quick responses, such as autonomous vehicles and remote healthcare services. Reduced latency improves the performance of smart home devices, facilitating instant communication between devices, thereby enhancing home automation capabilities.
Infrastructure modernization is essential for the successful deployment of 5G networks. This includes establishing new base stations and enhancing existing fiber optic connections to support increased data traffic. As cities and rural areas alike adapt to this next-generation technology, it holds significant implications for the integration of smart home systems, allowing for richer inter-device communication and better user experiences. The transition to 5G infrastructure is not merely a technological upgrade; it is a vital step towards creating fully connected and automated living environments.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Its Role in Smart Homes
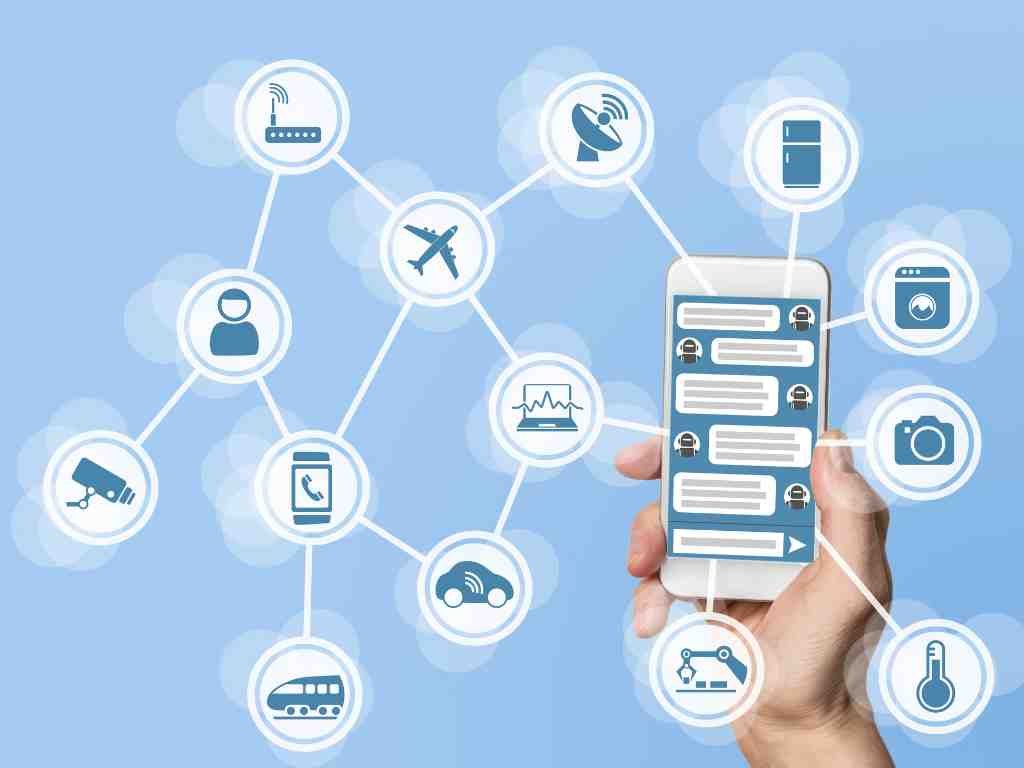
The Internet of Things (IoT) represents a transformative concept that connects everyday objects to the internet, facilitating communication and data exchange between devices. In the context of smart homes, IoT plays a pivotal role by enabling a wide range of products to interact seamlessly with one another, creating an interconnected living environment. Common devices include smart thermostats, security cameras, door locks, and voice-activated home assistants. These devices utilize sensors and software to collect data, allowing users to control various aspects of their homes remotely.

For example, smart thermostats can learn a household’s temperature preferences and adjust accordingly, leading to energy savings and enhanced comfort. Security cameras equipped with IoT technology provide real-time monitoring and alerts, increasing the safety of homes and allowing homeowners to keep an eye on their property from virtually anywhere. Home assistants, which respond to voice commands, can manage other connected devices, provide information, and automate tasks, thus streamlining daily activities.
- Echo Hub — An easy-to-use Alexa-enabled control panel for your smart home devices—just ask Alexa or tap the display to control lights, smart plugs, camera feeds, and more.
- Streamline your smart home — Customize the controls and widgets, displayed on your dashboard to quickly adjust devices, view cameras, start routines, and more.
- Works with thousands of Alexa compatible devices — Compatible with thousands of connected locks, thermostats, speakers, and more. WiFi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, Matter, Sidewalk and Thread devices sync seam…
The interaction among these devices typically occurs through Wi-Fi or mobile networks, which serve as conduits for data transmission. This communication enables automation features, such as creating routines that trigger specific actions based on user preferences or external factors. However, the integration of IoT into smart homes is not without challenges. Concerns regarding data privacy and security arise, as these devices often require access to personal information to function effectively. Furthermore, compatibility issues between various brands and devices can complicate the user experience and limit the overall benefits of a connected home ecosystem.
Despite these challenges, the advantages of integrating IoT into smart homes are substantial. Improved energy efficiency, enhanced security, and elevated convenience are just a few of the notable benefits that contribute to making modern living more efficient and enjoyable. As technology advances, the IoT’s role in shaping smart homes will continue to evolve, addressing current challenges while maximizing the potential of connected devices.
Synergistic Effects of 5G and IoT on Smart Home Innovation
The convergence of 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) is fundamentally transforming the landscape of smart homes, enabling a more cohesive and efficient connected environment. 5G, with its exceptional speed and low latency, enhances the utility of IoT devices, allowing for near-instantaneous communication and response times. This capability is crucial for smart home applications that rely on real-time data processing to function effectively. Appliances, security systems, and smart lighting systems can operate seamlessly, creating a more responsive home environment.

One of the standout advantages of 5G connectivity is its ability to support an unprecedented number of devices simultaneously. Traditional networks often struggle to accommodate the vast array of smart devices typically found in modern homes. However, 5G’s higher bandwidth capacity allows them to thrive, facilitating a wide range of connected technologies. From smart thermostats to security cameras, homeowners can integrate numerous devices without the risk of network congestion, leading to an enhanced user experience and greater overall efficiency.
- True 2K HD aosu WirelessCam Pro System 2 Cam Kit – Security Camera Outdoor, Wireless Home Security System. 60% improved from 1080p. You can record videos and capture photos with picture-perfect detail…
- 166° Ultra-Wide-Angle – aosu WirelessCam Pro adoptes 7 pieces of advanced ultra-clear and wide angle lens, giving you an ultra-wide view of your property, maximum correcting the image to remove fishey…
- Smart Alerts, Quicker Action – Receive instant notifications for people coming, passing, staying. With quick preview image so you can judge and react quickly to potential threats, our wireless securit…
The capabilities of 5G also promote innovative applications in smart homes. For instance, smart security systems equipped with 5G can deliver real-time video feeds with minimal delay, enhancing safety and allowing homeowners to monitor their properties remotely. Similarly, home automation systems can be controlled and monitored from virtually anywhere, fostering a more flexible and convenient lifestyle. Another practical example is smart refrigerators that can optimize food inventory management by connecting with grocery delivery services in real-time.
The partnership between 5G and IoT empowers the evolution of smart homes into dynamic, interconnected ecosystems. This synergy not only amplifies the functionality of individual devices but also paves the way for groundbreaking innovations that redefine domestic living. The continued advancement of these technologies will likely unveil even more transformative applications, enriching our daily lives with improved convenience, security, and efficiency.
Future Trends and Considerations for Smart Homes
The rapid advancements in 5G technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) are set to shape the future of smart homes significantly. With increased bandwidth and lower latency provided by 5G, smart home devices can communicate more efficiently and effectively. This enhanced connectivity will facilitate a more integrated ecosystem of household devices, enabling seamless interactions between smart appliances, security systems, and climate control technologies. As devices become more interconnected, the potential for automated systems to learn user preferences and adjust settings autonomously will increase, creating a more personalized living environment.
Emerging standards and protocols, such as Matter and Thread, aim to standardize the way devices communicate in smart homes. These protocols will contribute to improved compatibility among different manufacturers, allowing consumers the flexibility to mix and match devices without compatibility issues. Consequently, as these frameworks gain traction, the diversity of smart home solutions is expected to expand, encouraging innovation and competition among suppliers. This will allow consumers to choose from a broader array of devices that can work together cohesively, enhancing the overall user experience.
However, along with the conveniences of connected devices come significant privacy and security concerns. As smart homes collect vast amounts of data regarding user behavior and preferences, safeguarding this information will be vital. Homeowners will need to be proactive in understanding the security features of their devices, ensuring they utilize strong passwords and regular software updates. Additionally, companies must prioritize transparent data usage policies and robust security measures to protect consumers from potential breaches. As smart homes evolve, maintaining user trust will be essential for the sustainable growth of this market.